Photo credit: Tesla
Remember when electric cars seemed like something out of a sci-fi movie? Well, folks, the future is now! Electric vehicles (EVs) are no longer just for tech enthusiasts; they’re quickly becoming a practical and popular choice for everyday drivers. They’re zipping around our neighborhoods, turning heads, and making us rethink the way we drive.
If you’ve been curious about EVs but haven’t taken the plunge, this article is for you. We’ll break down the benefits of going electric and address those lingering questions you might have.
Let’s take a practical look at the world of EVs, exploring the good, the bad, and the electrifying (pun intended).
Beyond the Pump: The Hidden Benefits of Owning an Electric Vehicle
Let’s talk about something we all love: saving money. And something else, we probably all care about the environment. Luckily, electric vehicles offer benefits on both fronts.
Lower Operating Costs: Your Wallet Will Thank You

Photo credit: Tesla
Let’s talk numbers, shall we? One of the most appealing aspects of owning an EV is the potential for significant cost savings over the vehicle’s lifetime. While the initial purchase price of an electric vehicle might be a bit higher than a similar gas-powered car, the savings start adding up quickly once you hit the road.
Electric vehicles can put a serious dent in your transportation costs. How? Well, for starters, electricity is generally much cheaper than gasoline. According to a 2023 study by the U.S. Department of Energy, the average cost to drive an EV 100 miles is about half the cost of driving a gasoline-powered car the same distance. That’s a difference that can really add up over time, especially if you do a lot of driving. Think about it – no more trips to the gas station where prices seem to change with the wind. Instead, you can charge your EV at home while you sleep, often at a fraction of the cost of filling up a gas tank.
But the savings don’t stop at the pump (or charging station, in this case). EVs have fewer moving parts than gas-powered cars, meaning fewer things that can break down. Say goodbye to expensive oil changes, transmission repairs, and other maintenance headaches that come with gas-powered vehicles. In fact, some studies estimate that EV owners can save up to 50% on maintenance costs over the lifetime of their vehicle.
Personal Experience: Minimal Maintenance with My Tesla
In my six years of owning a Tesla, I’ve barely had to do any maintenance beyond the usual tire rotations and windshield washer fluid refills. For the first four years, the annual maintenance was even covered under the warranty, so I didn’t have to pay a dime.
Compared to my previous gas-powered car, which seemed to constantly need oil changes, brake pad replacements, and other repairs, my Tesla has been a breath of fresh air. The lower maintenance costs are a significant advantage of owning an EV and contribute to the overall cost savings over the lifetime of the vehicle.
Zero Emissions: A Breath of Fresh Air

Photo credit: Rivian
The most obvious environmental benefit of EVs is their lack of tailpipe emissions. Unlike gas-powered cars, which spew harmful pollutants into the air we breathe, EVs produce zero emissions while driving. This translates to cleaner air, especially in urban areas where air pollution is a major concern. Fewer emissions mean less smog, fewer respiratory problems, and a healthier environment for everyone.
Smaller Carbon Footprint: A Step Towards a Sustainable Future

Photo credit: Tesla
Even when you factor in the electricity used to charge EVs, they still typically have a smaller carbon footprint than gasoline-powered cars. The electricity grid is becoming increasingly cleaner, with more renewable energy sources like solar and wind power coming online. As the grid gets greener, the environmental impact of EVs will only improve further.
Plus, many EV owners choose to charge their vehicles with renewable energy sources, either through home solar panels or by selecting green energy options from their utility providers. This further reduces the carbon footprint of EVs, making them an even more sustainable choice.
Smooth, Silent, and Speedy: The Driving Experience of an EV
One of the most surprising and enjoyable aspects of owning an electric vehicle is the unique driving experience it offers. Unlike traditional gas-powered cars, EVs offer a smooth, quiet, and surprisingly powerful ride that will change how you think about getting from point A to B.
Instant Torque: Feel the Power

Photo credit: Tesla
Electric motors deliver instant torque, which means you get that satisfying surge of power the moment you press the accelerator. There’s no waiting for the engine to rev up or gears to shift. This translates to quicker acceleration, smoother takeoffs, and a more responsive driving feel overall. It’s a bit like having a sports car at your disposal, even if you’re driving a family-friendly SUV.
Silent Running: Enjoy the Peace
Say goodbye to the roar of the engine and the constant hum of a gas-powered car. Electric vehicles are incredibly quiet, creating a peaceful and relaxing driving environment. You’ll be able to enjoy conversations with your passengers, listen to your favorite music without cranking up the volume, and appreciate the sounds of nature as you cruise down the road. Some people find the quietness of EVs a bit eerie at first, but most quickly come to appreciate the tranquility.
Regenerative Braking: Harnessing Energy
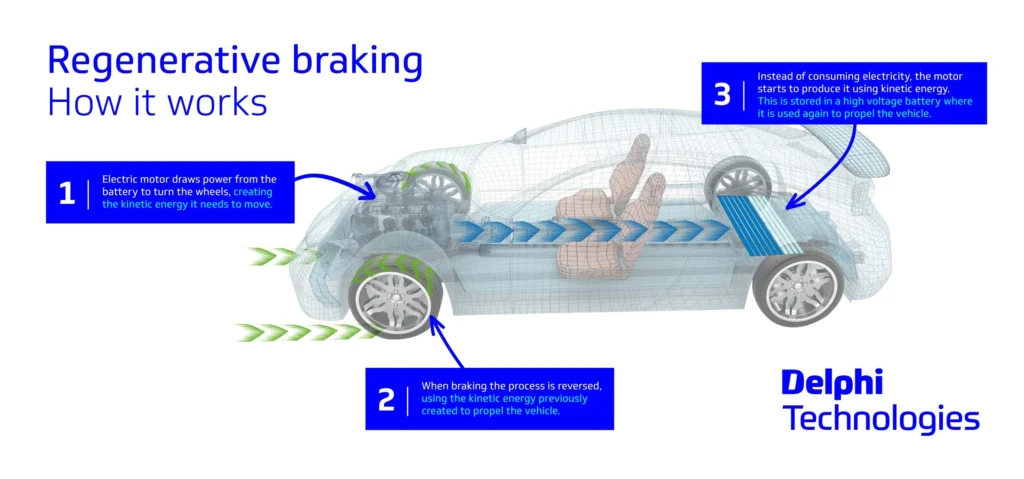
Photo credit: Vinfast Auto
Many EVs come equipped with regenerative braking, a technology that captures energy normally lost during braking and converts it back into electricity to recharge the battery, helping to extend your driving range. This not only improves the car’s efficiency but also creates a unique driving experience. When you lift your foot off the accelerator, the car starts to slow down gently, and you can even come to a complete stop without touching the brake pedal in some cases. Regenerative braking can take some getting used to. However, once you get the hang of it, it becomes a seamless and efficient part of the driving experience.
Tech-Savvy Features: A Glimpse into the Future

Photo credit: Tesla
Electric vehicles are often packed with the latest technology features, such as large touchscreen displays, advanced driver-assistance systems, and over-the-air software updates. These features can enhance safety, convenience, and overall enjoyment of the driving experience. Some EVs even offer semi-autonomous driving capabilities, allowing you to take your hands off the wheel (temporarily, of course) and let the car handle some of the driving tasks.
But What About…? Debunking Common Electric Vehicle Myths
Electric vehicles have come a long way, but there are still a few myths and misconceptions floating around that might make you hesitate. Let’s clear the air and separate fact from fiction.
Myth #1: EVs Don’t Have Enough Range for My Needs

Photo credit: Rivian
This is perhaps the most common concern about electric vehicles, but it’s becoming less and less relevant as technology advances. While it’s true that earlier EV models had limited range, today’s electric vehicles can easily travel 200 to 300 miles on a single charge, and some high-end models can go even further.
For most daily commutes and errands, this range is more than sufficient. And with the growing network of charging stations across North America, even longer road trips are becoming increasingly feasible.
Myth #2: Charging an EV Takes Forever

Photo credit: Rivian
Charging times have also improved significantly in recent years. While it’s true that charging an EV takes longer than filling up a gas tank, the process is much more convenient than you might think.
Most EV owners simply plug in their cars at home overnight, waking up to a full battery every morning. And even if you need to charge on the go, fast-charging stations can add a significant amount of range in just 30 minutes. As charging technology continues to evolve, we can expect even faster charging times in the future.
Myth #3: EVs Are Too Expensive

Photo credit: Tesla
While the initial purchase price of an electric vehicle might be a bit higher than that of a similar gas-powered car, the total cost of ownership is often lower. This is due to the lower operating and maintenance costs of EVs, as we discussed earlier. It’s also important to consider the long-term savings potential of EVs. With rising gas prices and the potential for future fuel shortages, the cost of owning a gas-powered car is likely to increase over time.
Myth #4: EVs Are Only for City Dwellers

Photo credit: Rivian
While electric cars are certainly great for city driving, with their compact size and easy handling, they are not limited to urban environments. As mentioned earlier, the range of modern EVs is more than enough for most daily commutes, including those in suburban or rural areas. With the expanding network of charging stations, long-distance travel is also becoming increasingly viable. Plus, many EV models now come in SUV and truck configurations, catering to the needs of families and outdoor enthusiasts.
Myth #5: EVs Aren’t as Safe as Gas-Powered Cars
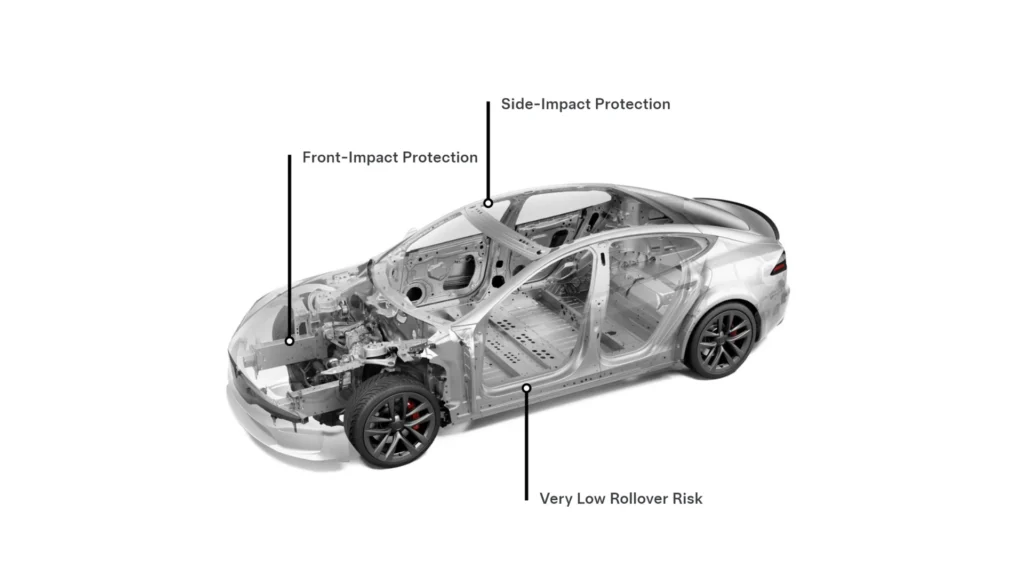
Photo credit: Tesla
Safety is a top priority for any vehicle purchase, and EVs are no exception. Electric vehicles undergo rigorous safety testing, just like their gas-powered counterparts. In fact, many EVs have received top safety ratings from organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). Studies also suggest that EVs might even be safer due to their lower center of gravity (thanks to the heavy battery pack) and lack of flammable fuel.
EVs are also equipped with various safety features, safety features like automatic emergency braking, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control, which can further enhance safety on the road. Many newer models also come with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), which can help prevent accidents and protect occupants in the event of a collision.
Myth #6: EVs Are More Prone to Fires Than Gas-Powered Cars
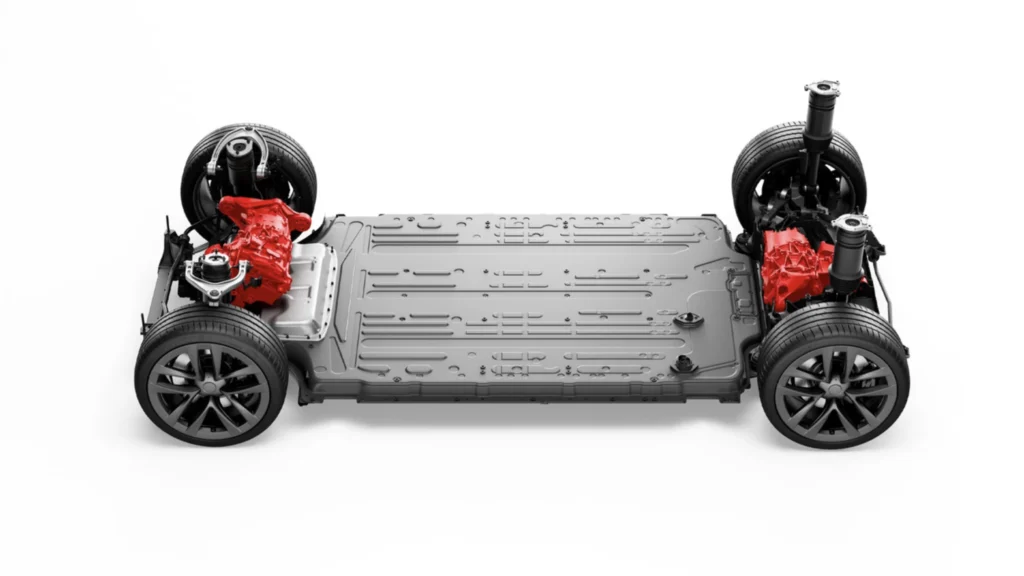

Photo credit: Tesla
While high-profile incidents involving electric vehicle (EV) fires may have grabbed headlines, the data tells a different story. Studies have consistently shown that EVs have a lower incidence of fires compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), the rate of fires in traditional gas-powered vehicles is significantly higher than in electric vehicles.
The lithium-ion batteries used in EVs can pose a fire risk under certain conditions, but so can the flammable liquids and complex engine systems found in gas-powered cars. The key is to understand the potential risks associated with both types of vehicles and take appropriate precautions, such as following the manufacturer’s charging guidelines.
Myth #7: There Aren’t Enough Charging Stations
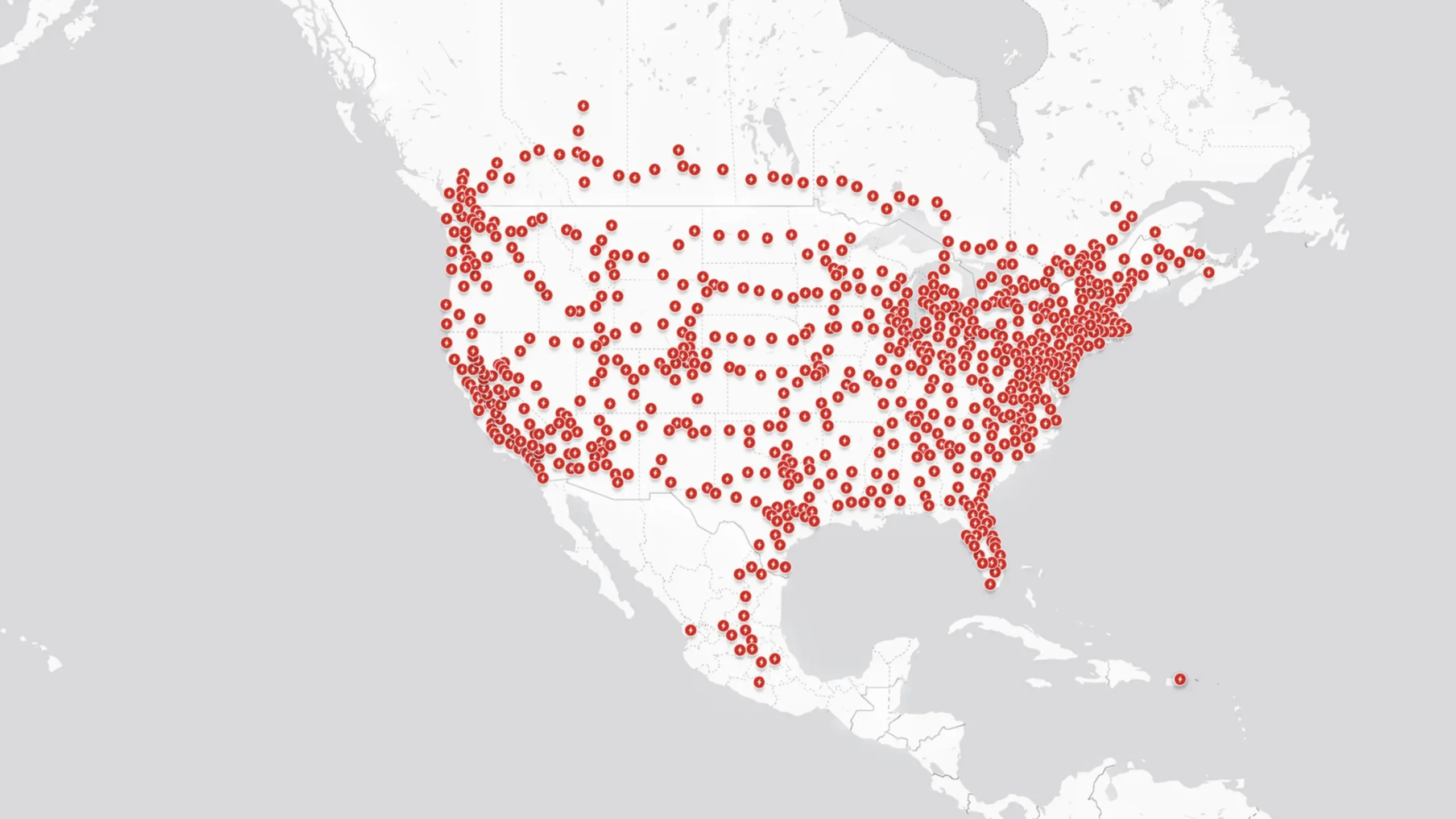
Photo credit: Tesla
While the charging infrastructure isn’t as widespread as gas stations (yet!), it’s growing rapidly. New charging stations are popping up all the time, both in cities and along major highways. Many workplaces, apartment buildings, and even some grocery stores now offer EV charging. Plus, most EV owners charge their vehicles at home, so public charging isn’t always necessary.
Various apps and online resources can help you locate charging stations and plan your trips accordingly. As more people adopt EVs, the charging infrastructure will only continue to expand, making it even easier to find a place to plug in.
Myth #8: EVs Are Bad for the Power Grid
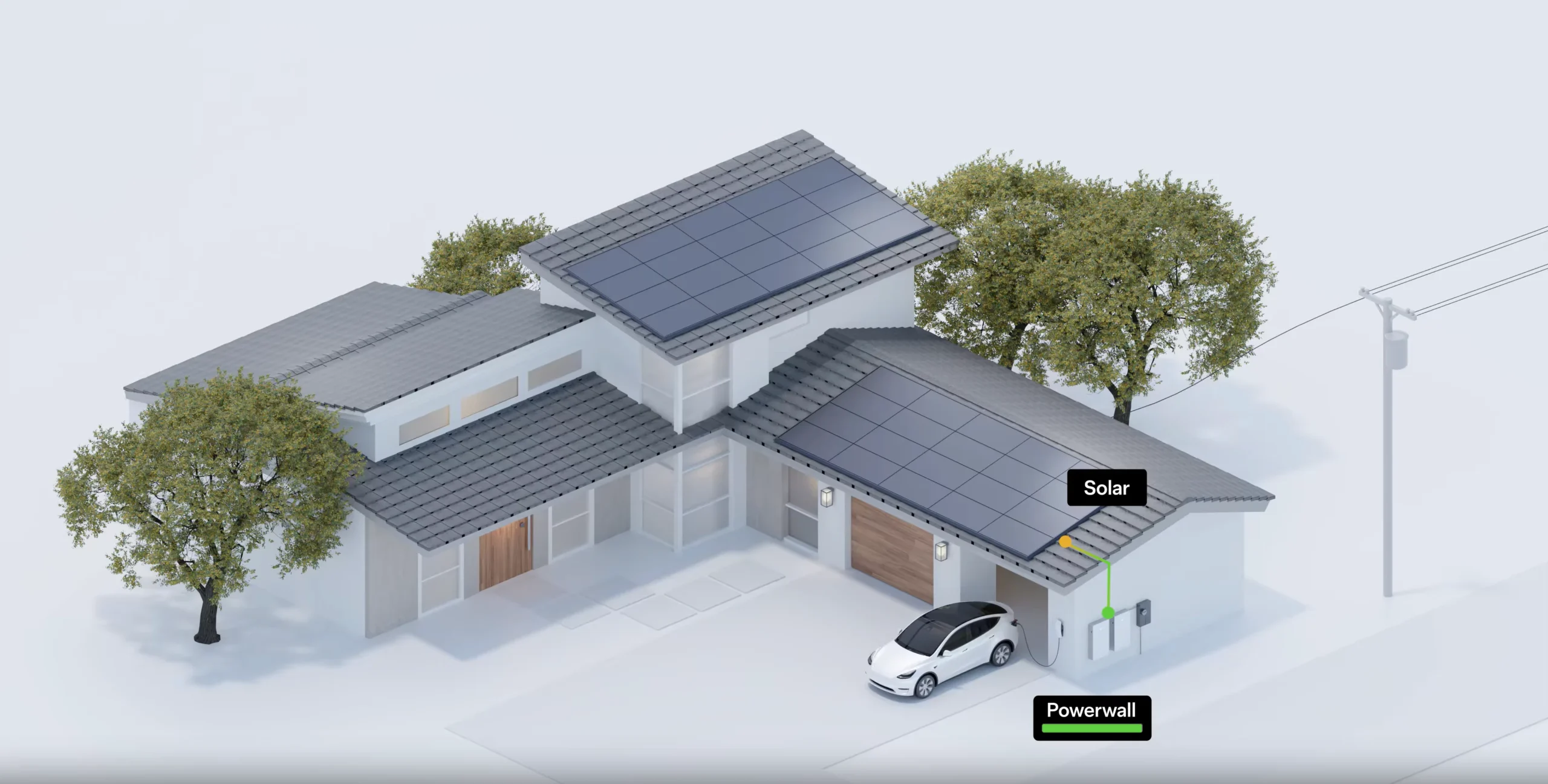


Photo credit: Tesla
There’s a common misconception that widespread adoption of electric vehicles would overload the power grid. However, studies have shown that the grid has the capacity to handle a significant increase in EV charging, especially with smart charging strategies that optimize charging times and distribute the load. Also, the growth of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is further strengthening the grid’s capacity to handle the demand from EVs.
Myth #9: EVs Are Bad for the Environment Because of Battery Production
While it’s true that the production of EV batteries has an environmental impact, it’s important to look at the bigger picture. EVs have a significantly lower carbon footprint over their lifetime compared to gas-powered cars, even when factoring in battery production.
Furthermore, efforts are being made to make battery production more sustainable, with initiatives focused on recycling and reducing the environmental impact of mining and manufacturing processes. As technology advances, we can expect even greener and more efficient EV batteries in the future.
Myth #10: EVs Don’t Perform Well in Cold Weather

Photo credit: Tesla
It’s true that cold weather can affect the performance and range of electric vehicles, but the impact is often exaggerated. Like any battery-powered device, EV batteries operate more efficiently in warmer temperatures. However, modern EVs are designed with cold weather in mind, and advancements in battery technology have significantly improved their performance in colder climates.
Here’s a breakdown of how cold weather can affect EVs and what you can do to mitigate the impact:
- Reduced Range: Cold temperatures can decrease the range of an EV by 10-20%, depending on the severity of the cold and how you use the vehicle’s heating and other features. This is because the battery’s chemical reactions slow down in cold weather, and more energy is needed to heat the cabin and battery.
- Slower Charging: Charging times can also be affected by cold weather, as the battery’s ability to accept a charge can be reduced at lower temperatures. However, most modern EVs have thermal management systems that help maintain the battery’s optimal temperature for charging.
It’s important to note that gas-powered cars also experience reduced efficiency in cold weather. Cold temperatures can thicken engine oil, making it harder for the engine to turn over and reducing fuel economy.
Tips for Maximizing EV Performance in Cold Weather:
- Preconditioning: If your EV has a preconditioning feature, use it to warm up the battery and cabin while the car is still plugged in. This will help to optimize battery performance and ensure a comfortable driving experience.
- Park Indoors: Whenever possible, park your EV in a garage or other sheltered location to protect it from the elements.
- Drive Conservatively: Avoid hard acceleration and excessive speeding, as these can drain the battery more quickly in cold weather.
- Plan Your Trips: If you’re planning a long trip in cold weather, be sure to factor in the potential for reduced range and plan your charging stops accordingly.
While cold weather does impact EV range, it’s not a dealbreaker for most drivers. With proper planning and charging strategies, EVs can still be a practical and reliable choice even in colder climates.
Personal Experience: A Tesla in a Canadian Winter? No Problem!
I can personally confirm the fact that EVs can handle extreme cold. I drove my Tesla for over a year in temperatures as low as -40°C (-40°F), and it performed admirably. While the range was slightly reduced, it was easily manageable with a bit of planning. In fact, I found my Tesla to be far more convenient than my previous gas-powered car during the winter months. The ability to preheat the cabin and defrost the windows remotely was a game-changer, especially when compared to the lengthy warm-up times and frozen windshields and steering wheel I experienced with my old car.
Range Anxiety No More: Charging Your EV and Planning Your Trips
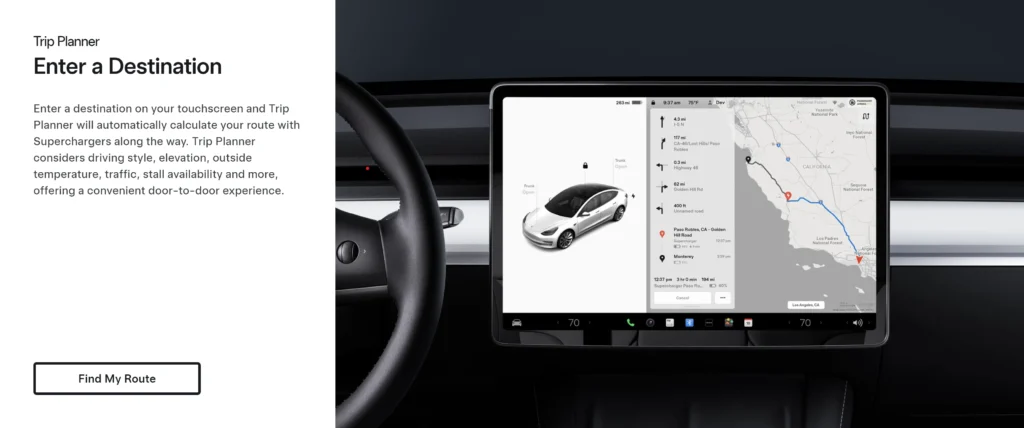
Photo credit: Tesla
One of the most frequently asked questions about electric vehicles is, “How far can I go on a single charge?” It’s a valid concern, and understanding the range of your EV and how to charge it is crucial for a smooth and enjoyable driving experience.
Range: How Far Can You Go?
The range of electric vehicles varies depending on the model, battery size, driving conditions, and other factors. However, most modern EVs offer a range of 200 to 300 miles on a single charge, which is more than enough for most daily commutes and errands. Some high-end models boast even longer ranges exceeding 400 miles.
It’s important to note that the advertised range is often based on ideal conditions, so your actual range may vary depending on factors like temperature, driving speed, terrain, and use of accessories like heating and air conditioning.
Charging: Fueling Up Your EV

Photo credit: Rivian
Charging an electric vehicle is different from filling up a gas tank, but it’s becoming increasingly convenient and accessible. Here are the main ways to charge your EV:
- Level 1 Charging (Home Charging): This is the slowest way to charge, using a regular 120-volt home outlet. It can take anywhere from 8 to 24 hours to fully charge an EV using Level 1 charging. However, it’s the most convenient option for overnight charging at home.
- Level 2 Charging (Home and Public): This is a faster charging method, using a 240-volt outlet similar to the ones used for electric dryers. Level 2 charging can fully charge an EV in 4 to 10 hours, depending on the model and battery size. Many homes and public charging stations offer Level 2 charging.
- DC Fast Charging (Public): This is the fastest charging method available, capable of adding significant range to an EV in just 30 minutes. DC fast chargers are typically found along major highways and at dedicated charging stations. However, not all EVs are compatible with DC fast charging.
Most EV owners primarily charge their vehicles at home using a Level 2 charger. This is the most convenient and cost-effective way to charge an EV, as you can simply plug in your car overnight and wake up to a full battery every morning.
Are There Enough Charging Stations?
While the charging infrastructure for electric vehicles is still a work in progress, it’s rapidly expanding, with thousands of charging stations now available across North America. Many public charging stations are located in convenient places like shopping centers, restaurants, and parking garages.
Tesla’s Supercharger Network: A Game-Changer for Long-Distance Travel
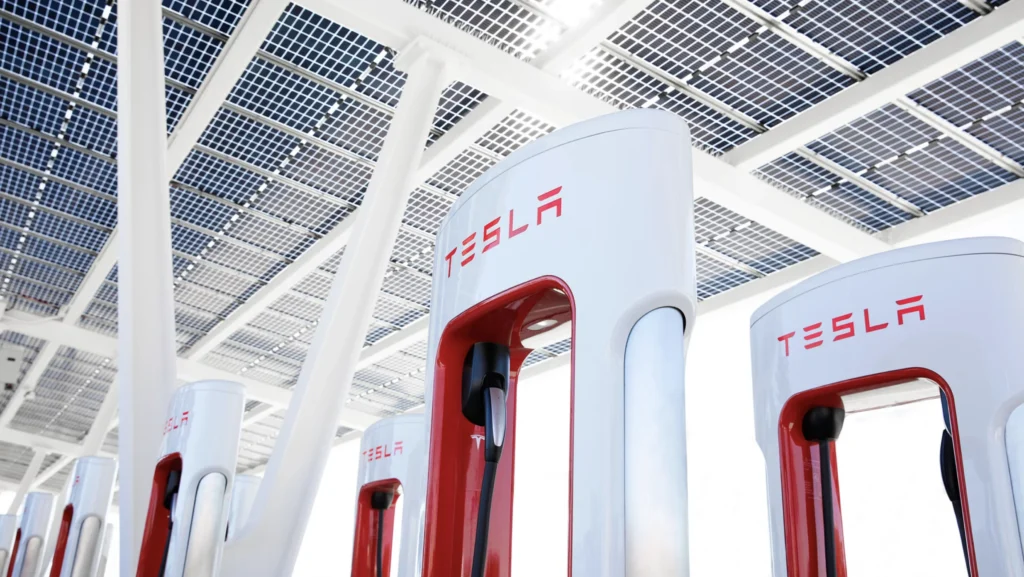

Photo credit: Tesla
One company that has been particularly proactive in building out its charging infrastructure is Tesla. Their Supercharger network, a network of fast-charging stations located along major highways and in popular destinations, has made long-distance travel in a Tesla a breeze.
In fact, as a Tesla owner for over six years, I can confidently say that the Supercharger network is convenient and reliable. When planning a road trip, the car’s navigation system automatically maps out the optimal route, including stops at Supercharger stations. These stops are strategically located near restaurants, shops, and other amenities, making it easy to grab a bite to eat or stretch your legs while your car charges. It’s actually a nice break from driving! I can’t speak for other electric car brands, but my experience with Tesla’s Supercharger network has been nothing short of fantastic.
The Electric Vehicle Revolution is Here to Stay

Photo credit: Tesla
Electric vehicles are no longer a futuristic concept – they’re a practical and increasingly popular choice for drivers across North America. With lower operating costs, reduced environmental impact, and an exhilarating driving experience, EVs offer a compelling alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
While concerns about range, charging, and cost still exist, the reality is that EVs are becoming more accessible and convenient than ever before. As technology continues to advance and charging infrastructure expands, the benefits of going electric will only become more apparent.
If you’re considering making the switch to an electric vehicle, there’s never been a better time to explore your options. Do your research, weigh the pros and cons, and take a test drive to experience the unique thrill of driving electric. Who knows, you might just find yourself joining the growing number of drivers who are embracing the electric vehicle revolution.
FAQs
What Happens if My Electric Vehicle Runs Out of Battery on the Road?
Running out of charge, while rare, can happen. Most EVs have a “turtle mode” that limits speed and features to help you reach a charging station. Roadside assistance can also help, either by providing a small charge or towing you to the nearest station. Just like with a gas car, planning your trips and being aware of charging locations is key.
Can Electric Vehicles Handle Extreme Weather Conditions Like Heavy Rain or Snow?
Yes, they can! Electric vehicles (EVs) are built to handle different kinds of weather, including heavy rain and snow. Their batteries are sealed and well-protected, and their weight distribution often provides good traction. In fact, some studies suggest that EVs might even have a slight advantage in snowy conditions due to their instant torque and smooth power delivery.
How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
Charging time depends on the battery size, the charging level, and the current state of charge. Level 1 charging (standard household outlet) can take 8-24 hours for a full charge, Level 2 charging (240V outlet) takes 4-8 hours, and DC fast charging (public stations) can add significant range in 30-40 minutes.
What is the lifespan of an electric vehicle battery?
EV batteries are designed to last for a significant portion of the vehicle’s lifespan. Most manufacturers offer warranties of 8-10 years or 100,000-150,000 miles on their batteries. Battery degradation is a natural process, but advancements in technology are constantly improving battery longevity.
Can I install an EV charger at home, and how much does it cost?
Yes, most EV owners install a Level 2 charger at home for convenient overnight charging. The cost varies depending on the charger model and installation complexity, but it typically ranges from $500 to $2,000. Many electric utilities offer rebates or incentives to offset the cost of purchasing and installing a home charger.
Can I take my EV on a road trip?
Absolutely! With the expanding network of fast-charging stations across North America, road trips in an EV are becoming increasingly common. Many EVs now offer ranges of 200+ miles on a single charge, and route planning apps can help you locate charging stations along your route.
What is vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, and how does it work?
V2G technology allows electric vehicles to act as a power source, feeding electricity back into the grid during peak demand periods or when renewable energy sources are intermittent. This can help stabilize the grid, reduce the need for fossil fuel power plants, and potentially generate income for EV owners.